Note Taking Methods: 7 Secret Methods of Studying
This post may contain affiliate links, which means I'll receive a commission if you purchase through my link, at no extra cost to you. Please read full disclosure here.
As an Amazon Affiliate I earn from qualifying purchases.
This post is all about note taking methods and explores the 7 secret methods of studying to help you improve your note-taking and studying for enhanced learning.
Blog Post Promise: In this guide, we will explore the 7 secret methods of studying that can transform your note-taking process and enhance your learning experience.
There are many ways to take notes, and it can be hard to figure out which one is best for you.
There are 7 secret methods, each with its own benefits and suitable for different learning styles and preferences.
By using these secret note taking methods in your studying, you can improve how well you understand, remember, and use what you learn.
Whether you like mind maps, outlines, or mnemonic devices, these methods will help you take better notes.
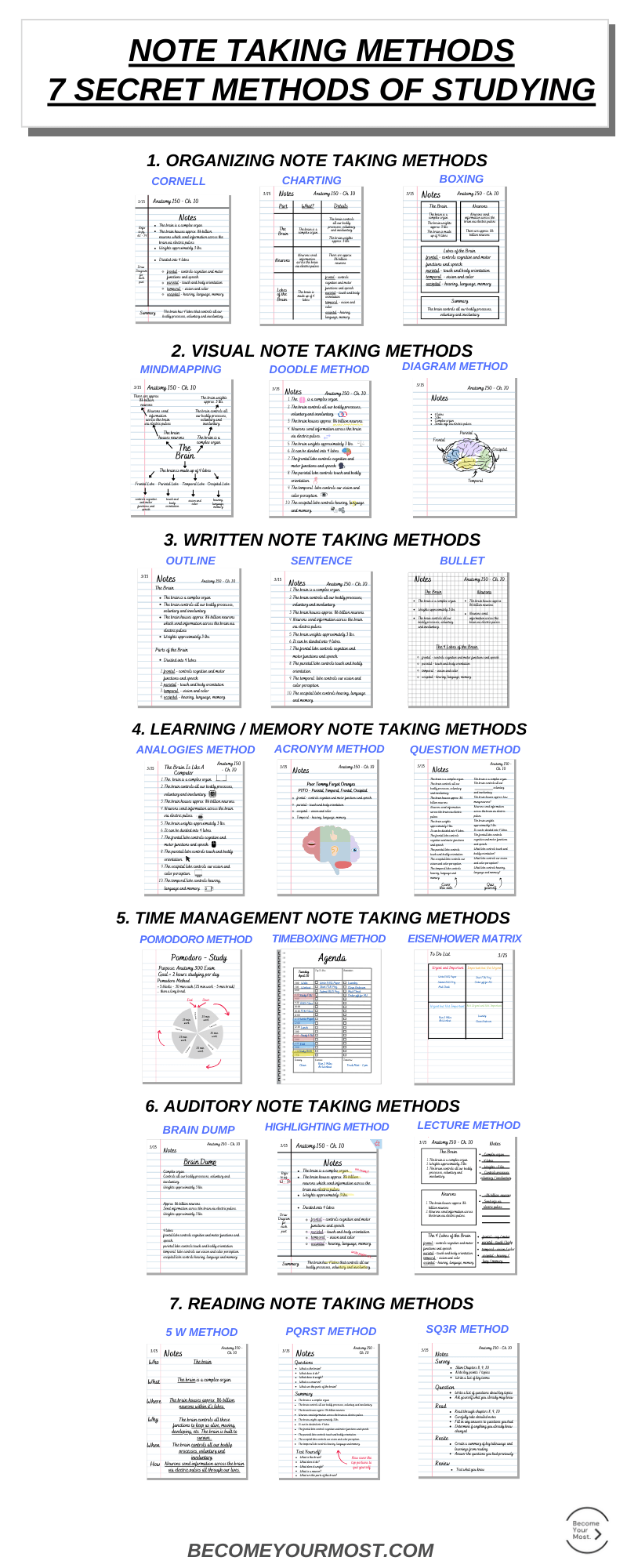
The 7 Secret Methods for Studying
There are 7 secret methods of studying for note taking methods:
Organizing
Visual
Written
Learning / Memory
Time Management
Auditory
Reading
Incorporating all 7 secret methods of studying is important because it allows for a comprehensive and well-rounded approach to learning.
Let’s dive into all different methods of note-taking for eaching method of study.
Note Taking Methods: The 7 Secret Methods of Studying
Note Taking Methods: 7 Secret Methods Of Studying
1. Organizing Note Taking Methods
Cornell Method:
Cornell Method
Cornell Method Definition: The Cornell Method is a note-taking system that involves dividing a note page into three sections: a narrow left column for cues and questions, a wider right column for note-taking, and a bottom section for summarizing key points.
Cornell Method Example: In the Cornell Method, you would write main ideas and supporting details in the right column, and then use the left column to jot down keywords or questions that serve as cues for reviewing the material later. Finally, you would summarize the main points in the bottom section.
Charting Method:
Charting Method Definition: The Charting Method is a note-taking technique that involves creating tables or charts to compare and organize information. It is useful for organizing data, making comparisons, and identifying patterns.
Charting Method Example: In the Charting Method, you can create columns and rows to categorize and compare information. This method is commonly used for recording data, making comparisons between different variables, and summarizing information in a visually appealing way.
Box-Method:
Box-Method Definition: The Box-Method involves visually organizing information using boxes or rectangles to represent different concepts, ideas, or categories.
Box-Method Example: In the Box-Method, you would write or draw individual ideas or concepts inside separate boxes and then connect them using lines or arrows to show relationships or connections. This method helps in visualizing the relationships between different elements or categories of information.
T-Method:
T-Method Definition: The T-Method involves dividing a note page into two sections, creating a T-shaped layout. The left side is used for jotting down questions, headings, or main ideas, while the right side is used for providing answers, details, or explanations.
T-Method Example: When using the T-Method, you would write questions or main ideas in the left column, and corresponding answers or details in the right column. This method helps in organizing information in a structured manner and facilitates easy review and revision.
Venn Diagrams:
Venn Diagrams Definition: Venn Diagrams are visual representations that show the relationship between different sets or groups through overlapping circles.
Venn Diagrams Example: When using Venn Diagrams, you would draw circles that represent different sets or categories, and the overlapping areas indicate commonalities or shared characteristics. This method helps in comparing and contrasting information or identifying relationships between different elements.
Hierarchy Method:
Hierarchy Method Definition: The Hierarchy Method involves organizing information in a hierarchical structure, starting from broad categories and moving to specific details.
Hierarchy Method Example: In the Hierarchy Method, you would start with main categories or concepts and then break them down into subcategories or supporting details. This method helps in understanding the relationships between different levels of information.
Matrix Method:
Matrix Method Definition: The Matrix Method is a note-taking technique that involves organizing information in a grid or matrix format to compare and categorize different elements.
Matrix Method Example: When using the Matrix Method, you would create a table or grid with rows and columns to categorize and compare information. This method is useful for organizing data, making comparisons, and identifying patterns.
Decision Tree Method:
Decision Tree Definition: The Decision Tree Method is a visual tool that helps in making decisions or determining the best course of action by mapping out different possible outcomes and choices.
Decision Tree Example: When using the Decision Tree Method, you would create a diagram that branches out with different choices or options, leading to different outcomes or decisions. This method facilitates decision-making and helps in understanding the consequences of different choices.
2. Visual Note Taking Methods
Mind Mapping Method:
Mind Mapping Definition: The Mapping Method, also known as concept mapping or mind mapping, involves visually representing ideas and their relationships using diagrams or graphical representations.
Mind Mapping Example: When using the Mapping Method, you would start with a central idea or concept and branch out to sub-ideas or related concepts using lines or arrows. This method helps to visually organize and connect information in a non-linear way.
Diagramming Method:
Diagramming Definition: The Diagramming Method involves using diagrams, flowcharts, or visual representations to explain relationships, processes, or concepts.
Diagramming Example: In the Diagramming Method, you would use shapes, arrows, and labels to represent different elements and their connections. This method is beneficial for illustrating complex concepts, explaining processes, or visualizing relationships.
Sketchnoting:
Sketchnoting Definition: Sketchnoting is a visual note-taking method that combines handwritten notes with symbols and illustrations to capture and convey information.
Sketchnoting Example: When using Sketchnoting, you would create visual representations and drawings alongside your written notes to summarize and highlight key points. This method helps in engaging with the material and making the notes more memorable and visually appealing.
Color-Coding Method:
Color-Coding Definition: The Color-Coding Method involves using different colors to categorize and organize information within your notes.
Color-Coding Example: When using the Color-Coding Method, you would assign specific colors to different categories, topics, or themes. This method helps in visually distinguishing and organizing information, making it easier to review and understand at a glance.
Doodle Method / Emoji Method:
Doodle Method Definition: The Doodle Method involves incorporating simple doodles and drawings alongside written notes to enhance understanding and memory.
Doodle Method Example: When using the Doodle Method, you would create small and simple illustrations, symbols, or doodles related to the content of your notes. These doodles serve as visual cues and aids in recalling information and making the notes more engaging and memorable.
Flowchart Method:
Flowchart Definition: The Flowchart Method uses visual representations, typically in the form of flowcharts, to illustrate processes, sequences, or decision trees.
Flowchart Example: In the Flowchart Method, you would use different shapes and arrows to depict steps, actions, or decisions within a process. This method is useful for understanding and visualizing complex sequences and decision-making processes.
3. Written Note Taking Methods
Outline Method:
Outline Method Definition: The Outline Method involves organizing notes hierarchically using headings, subheadings, and bullet points. It helps to create a structured and organized outline of the content.
Outline Method Example: When using the Outline Method, you would start with a main heading, then indent for subheadings and bullet points under each subheading. This method allows for easy identification of main ideas and supporting details in a hierarchical manner.
Sentence Method:
Sentence Method Definition: The Sentence Method involves writing notes in complete sentences, providing a more detailed and comprehensive record of the information.
Sentence Method Example: When using the Sentence Method, you would write down the main ideas and supporting details in complete, coherent sentences. This method is useful when capturing important details or when a more detailed record of the information is required.
Summary Method:
Summary Method Definition: The Summary Method involves condensing and summarizing the main ideas and key points of a lecture or text into a concise summary.
Summary Method Example: With the Summary Method, you would focus on identifying the most important concepts, facts, or arguments and then write a brief summary that captures the essence of the information. This method helps in synthesizing and retaining key information.
Two-Column Method:
Two-Column Method Definition: The Two-Column Method involves dividing a note page into two columns, one for main ideas or questions, and the other for supporting details or answers.
Two-Column Method Example: When using the Two-Column Method, you would write the main ideas, questions, or headings in the left column, and the corresponding details or answers in the right column. This method helps in organizing information and making connections between key ideas and supporting information.
Storytelling / Narrative Method:
Storytelling Method Definition: The Storytelling Method involves transforming information or concepts into a narrative or story-like format, making it more engaging and memorable.
Storytelling Method Example: When using the Storytelling Method, you would create a narrative that connects different pieces of information, concepts, or events. This method helps in retaining and recalling information through the power of storytelling.
SWOT Analysis Method:
SWOT Analysis Method Definition: SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) is a method for evaluating and analyzing the internal and external factors of a situation or organization.
SWOT Analysis Method Example: In SWOT Analysis, you would identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a particular subject, project, or organization. This method helps in assessing the current situation and making informed decisions.
Bullet Journal Method:
Bullet Journal Definition: The Bullet Journal Method is a customizable and organized note-taking system that uses bullet points, symbols, and signifiers to track tasks, events, and notes.
Bullet Journal Example: When using the Bullet Journal Method, you would create a system of bullet points, symbols, and trackers to categorize and organize your notes and tasks. This method allows for flexibility and personalization in note-taking and task management.
4. Learning / Memory Note Taking Methods
The Feynman Technique:
Feynman Technique Definition: The Feynman Technique is a learning and note-taking method named after the physicist Richard Feynman. It involves simplifying and explaining complex concepts in plain language to enhance understanding.
Feynman Technique Example: To apply the Feynman Technique, you would select a concept or topic and explain it in simple terms as if you were teaching it to someone unfamiliar with the subject. This method helps to identify gaps in understanding and reinforces comprehension.
Keyword Method:
Keyword Method Definition: The Keyword Method involves associating keywords or mental images with the information you want to remember.
Keyword Method Example: In the Keyword Method, you would identify keywords in the information and create mental images or associations that help you remember them. This method aids in recalling information by connecting it to memorable keywords or images.
Association Method:
Association Method Definition: The Association Method involves creating associations or connections between pieces of information to enhance memory and recall.
Association Method Example: When using the Association Method, you would link new information to existing knowledge or create mental connections between different pieces of information. This method helps in strengthening memory and facilitates retrieval.
Acronyms and Mnemonics:
Acronyms and Mnemonics Definition: Acronyms and Mnemonics are memory aids that use short words, phrases, or letters to help remember information.
Acronyms and Mnemonics Examples: When using Acronyms, you would create a word or phrase using the first letter of each item or concept you want to remember. For Mnemonics, you would create associations or mental images to remember information. These methods aid in memorization and recall.
Analogies Method:
Analogies Method Definition: The Analogies Method involves understanding and explaining new information by drawing comparisons to familiar concepts or ideas.
Analogies Method Example: When using the Analogies Method, you would compare new or unfamiliar concepts to familiar concepts or ideas. This method helps in understanding and explaining complex information by relating it to something known and familiar.
Index Card Method:
Index Card Method Definition: The Index Card Method involves using index cards to capture and organize small pieces of information, ideas, or key points.
Index Card Method Example: When using the Index Card Method, you would write individual pieces of information or ideas on separate index cards. These cards can be easily shuffled, rearranged, and grouped as needed, making it convenient to study or review specific topics.
Spaced Repetition Method:
Spaced Repetition Method Definition: The Spaced Repetition Method is a learning technique that involves reviewing and revisiting information at increasing intervals over time to enhance long-term retention and recall.
Spaced Repetition Example: When using the Spaced Repetition Method, you would initially study a set of flashcards or notes. As you review the material, you identify the cards or topics that you struggle with or find more challenging. Instead of continuously reviewing all the material, you focus on these difficult cards or topics more frequently, spacing the repetitions closer together. As you gain mastery and familiarity with these challenging items, you gradually increase the spacing between repetitions. This method takes advantage of the spacing effect, which suggests that spacing out learning sessions over time improves long-term retention and recall. By strategically reviewing and revisiting challenging material at optimal intervals, you can enhance your overall learning and memory retention.
Question Method:
Question Method Definition: The Question Method is a note-taking technique that involves transforming information into a series of questions and answers to facilitate active learning and retention.
Question Method Example: When using the Question Method, you would convert key points, concepts, or information into questions. Next, you would provide concise answers or explanations to these questions. This method promotes active engagement with the material, encourages critical thinking, and aids in recall during review and study sessions.
5. Time Management Note Taking Methods
Pomodoro Technique:
Pomodoro Technique Definition: The Pomodoro Technique is a time management method that involves breaking work into focused intervals, typically 25 minutes, separated by short breaks.
Pomodoro Technique Example: When using the Pomodoro Technique, you would work on a specific task or activity for 25 minutes (known as a "Pomodoro") and then take a short break of around 5 minutes. After completing a set number of Pomodoros, typically four, you can take a longer break. This method helps in managing time effectively and maintaining focus.
Timeboxing Method:
Timeboxing Method Definition: The Timeboxing Method involves allocating specific time periods, or "boxes," for different tasks or activities.
Timeboxing Method Example: When using the Timeboxing Method, you would assign fixed time blocks for different tasks or activities, ensuring that you dedicate a specific amount of time to each. This method helps in prioritizing tasks, managing time effectively, and maintaining a structured schedule.
The Eisenhower Matrix:
The Eisenhower Matrix Definition: The Eisenhower Matrix, also known as the Urgent-Important Matrix, is a time management and prioritization tool that helps in categorizing tasks based on urgency and importance.
The Eisenhower Matrix Example: When using the Eisenhower Matrix, you would divide tasks into four categories: Urgent and Important, Important but Not Urgent, Urgent but Not Important, and Not Urgent and Not Important. This method helps in prioritizing tasks effectively and focusing on activities that align with long-term goals.
The Pareto Principle:
Pareto Principle Definition: The Pareto Principle, also known as the 80/20 rule, states that roughly 80% of the effects come from 20% of the causes.
Pareto Principle Example: When using the Pareto Principle, you would focus on identifying and prioritizing the most critical or impactful tasks or factors that contribute to desired outcomes. This method helps in maximizing productivity and efficiency by concentrating efforts on the most significant factors.
The S.M.A.R.T. Goal Method:
S.M.A.R.T. Goal Method Definition: The S.M.A.R.T. Goal Method is a framework for setting and achieving goals that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
S.M.A.R.T. Goal Method Example: When using the S.M.A.R.T. Goal Method, you would set goals that are well-defined, quantifiable, attainable, relevant to your objectives, and have a specific timeframe for completion. This method helps in setting clear goals and increasing the likelihood of success.
The MoSCoW Method:
MoSCoW Method Definition: The MoSCoW Method is a prioritization technique used in project management to categorize requirements or tasks based on their importance and urgency.
MoSCoW Method Example: When using the MoSCoW Method, you would classify requirements or tasks into four categories: Must have, Should have, Could have, and Won't have. This method helps in prioritizing resources and efforts on essential tasks or requirements to ensure successful project completion.
6. Auditory Note Taking Methods
Lecture Method:
Lecture Method Definition: The Lecture Method involves actively listening and taking notes during a lecture or presentation to capture key information and concepts.
Lecture Method Example: When using the Lecture Method, you would listen attentively to the speaker, identify and write down main ideas, supporting details, and important concepts. This method helps in retaining and reviewing information presented in a lecture or presentation.
Brain Dump Method:
Brain Dump Method Definition: The Brain Dump Method involves quickly and freely jotting down all thoughts, ideas, and information related to a particular topic or task without worrying about organization or structure.
Brain Dump Method Example: When using the Brain Dump Method, you would take a blank piece of paper or a digital document and write down everything that comes to mind regarding a specific topic or task. This can include thoughts, ideas, to-do items, or any relevant information. The goal is to empty your mind and capture all relevant information without judgment or concern for organization. Once completed, you can review and organize the information into a more structured format if desired. The Brain Dump Method helps in decluttering the mind, overcoming mental blocks, and capturing all relevant information for later processing and organization.
Highlighting and Underlining Method:
Highlighting and Underlining Method Definition: The Highlighting and Underlining Method involves marking important information or key points using highlighters or underlining in written texts or documents.
Highlighting and Underlining Method Example: When using the Highlighting and Underlining Method, you would use different colors or underline important phrases, sentences, or concepts to make them stand out. This method helps in quickly identifying and reviewing essential information in written materials.
Quick Notes Method:
Quick Notes Method Definition: The Quick Notes Method involves capturing brief and concise notes that focus on key points, keywords, or main ideas.
Quick Notes Method Example: When using the Quick Notes Method, you would write down essential information in a concise and summarized format, using bullet points, abbreviations, or keywords. This method helps in quickly reviewing and recalling key information.
Recording Method:
Recording Method Definition: The Recording Method involves using audio or video recording devices to capture lectures, presentations, or discussions for later review.
Recording Method Example: When using the Recording Method, you would use a recording device to capture audio or video of lectures, presentations, or discussions. This method allows for in-depth review and ensures that you don't miss any important information during note-taking.
7. Reading Note Taking Methods
SQ3R Method:
SQ3R Method Definition: The SQ3R Method is a systematic approach to reading and studying, involving five steps: Survey, Question, Read, Recite, and Review.
SQ3R Method Example: When using the SQ3R Method, you would start by surveying the text, skimming headings and summaries. Then, you generate questions based on the material, read the text actively, recite or summarize the information, and finally, review the material to reinforce understanding.
PQRST Method:
PQRST Method Definition: The PQRST Method is an active reading and note-taking technique that involves Preview, Question, Read, Summarize, and Test.
PQRST Method Example: When using the PQRST Method, you would start by previewing the material, generating questions, actively reading, summarizing the information, and testing your understanding through self-assessment. This method enhances comprehension and retention.
The 5 W's Method:
5 W's Method Definition: The 5 W's Method involves asking and answering the questions: Who, What, Where, When, and Why, to gather comprehensive information.
5 W's Method Example: When using the 5 W's Method, you would systematically ask and answer the questions: Who is involved? What happened or is happening? Where did it take place or will take place? When did it happen or will happen? Why did it happen or is it happening? This method helps in collecting essential details and gaining a complete understanding of a topic or situation.
The 6 Thinking Hats Method:
6 Thinking Hats Method Definition: The 6 Thinking Hats Method is an information gathering and decision-making technique developed by Edward de Bono. It involves considering different perspectives or modes of thinking to explore a topic or solve problems.
6 Thinking Hats Method Example: When using the 6 Thinking Hats Method, you would metaphorically wear different "hats" or roles, each representing a different perspective or mindset (e.g., logical, emotional, creative, critical, etc.). By consciously switching between these hats, you can explore a topic comprehensively and make more well-rounded decisions.
Why Should You Use The 7 Secret Methods for Studying
Each method offers unique benefits and caters to different learning styles and preferences.
Organizing: Organizing note-taking methods, such as the Cornell Method or the Charting Method, help in structuring and categorizing information, making it easier to review and understand.
Visual: Visual note-taking methods, like the Mind Mapping Method or the Diagramming Method, enhance understanding by visually representing relationships and connections between concepts.
Written: Written note-taking methods, such as the Outline Method or the Sentence Method, provide a detailed and organized record of information, aiding in retention and comprehension.
Learning/Memory: Learning and memory note-taking methods, such as the Feynman Technique or the Keyword Method, optimize memory retention and recall by employing techniques like simplification, associations, and mnemonic devices.
Time Management: Time management note-taking methods, like the Pomodoro Technique or the Eisenhower Matrix, help in managing time effectively, prioritizing tasks, and maintaining focus and productivity.
Auditory: Auditory note-taking methods, like the Lecture Method or the Brain Dump Method, facilitate active listening and capture of key information during lectures or discussions.
Reading: Reading note-taking methods involve strategies for annotating, highlighting, and summarizing texts, enhancing comprehension and retention.
By incorporating all 7 secret methods of studying, individuals can leverage the strengths of each method and tailor their note-taking approach to their own learning style.
This holistic approach promotes better understanding, retention, and application of knowledge, ultimately leading to more effective and efficient studying.
The 7 Secret Methods of Studying | Learning Styles
The 7 secret methods for studying can be adapted and utilized by different types of learners based on their preferred study methods.
Here's a breakdown of how each method can be applied to different learning styles:
Organizing Method:
Visual Learners: Visual learners can benefit from using visual aids such as diagrams, charts, and graphs to organize and categorize information.
Auditory Learners: Auditory learners can verbally explain the organization of information to a study partner or record themselves discussing the main ideas and concepts.
Kinesthetic Learners: Kinesthetic learners can physically manipulate study materials, such as arranging flashcards or creating physical representations of concepts, to understand the organization.
Visual Note Taking Methods:
Visual Learners: Visual learners can use mind maps, diagrams, and sketches to create visual representations of information and establish connections between ideas.
Auditory Learners: Auditory learners can use color-coding and visual cues to enhance their understanding of information. They can also verbally describe their visual notes to reinforce learning.
Kinesthetic Learners: Kinesthetic learners can enhance their visual note-taking by incorporating physical movements or gestures while creating their visual representations.
Written Note Taking Methods:
Visual Learners: Visual learners can benefit from using different writing styles, such as bullet points or summaries, to organize their written notes. They can also use highlighters or different fonts to emphasize important information.
Auditory Learners: Auditory learners can read their written notes aloud or record themselves explaining the concepts in their own words to reinforce understanding.
Kinesthetic Learners: Kinesthetic learners can engage with written notes by physically writing them out or using hands-on manipulatives like index cards or sticky notes.
Learning / Memory Note Taking Methods:
Visual Learners: Visual learners can create visual mnemonics, associations, or mental images to aid in memory recall. They can also utilize visual representations, such as flowcharts or decision trees, to understand and remember complex processes.
Auditory Learners: Auditory learners can create rhymes, songs, or mnemonics that incorporate auditory elements to enhance memory retention. They can also explain the concepts to others or engage in discussions to reinforce learning.
Kinesthetic Learners: Kinesthetic learners can engage in hands-on activities, such as creating physical models or participating in interactive learning experiences, to reinforce memory recall.
Time Management Note Taking Methods:
Visual Learners: Visual learners can use visual tools like calendars, timelines, or Gantt charts to plan and manage their study time effectively. They can also create color-coded schedules or utilize visual reminders for better time management.
Auditory Learners: Auditory learners can use audio recordings or verbal reminders to stay organized and manage their study time effectively. They can also engage in discussions or study groups to help structure their time.
Kinesthetic Learners: Kinesthetic learners can benefit from physically organizing their study materials, creating physical timers or using tactile reminders to manage their time effectively.
Auditory Note Taking Methods:
Visual Learners: Visual learners can enhance their auditory note-taking by incorporating visual cues or diagrams alongside their written notes. They can also create visual summaries or mind maps based on the auditory information.
Auditory Learners: Auditory learners can focus on actively listening during lectures or discussions, using keywords or short phrases to capture essential information. They can also record and replay the audio to reinforce understanding.
Kinesthetic Learners: Kinesthetic learners can engage in physical movements, such as drawing or doodling, while listening to auditory information to aid in memory retention.
By understanding their preferred learning style and adapting the study methods accordingly, learners can optimize their note-taking strategies and enhance their overall learning experience
This post was all about exploring different note taking methods and techniques for various purposes.
Each method offers unique benefits and can be adapted to different learning styles, including visual, auditory, and kinesthetic preferences. By understanding your preferred learning style and applying the appropriate note-taking method, you can enhance comprehension, retention, and overall learning effectiveness.
Remember, effective note-taking is not a one-size-fits-all approach. It's important to experiment with different methods, adapt them to your needs, and find what works best for you.
By doing so, you can transform your note-taking experience into an effective tool for enhancing understanding, retention, and overall academic or professional success.